Acids, Bases and Salt
ACIDS:
·
The
substance which taste sour contain acid and substance are called acidic
substance. Some of naturally occurring acidic substance are:- lemon juice,
orange juice, vinegar and curd.
·
Acids
are corrosive in nature and are soluble in water.
·
Acids turn red litmus to blue.
·
Release H+ ions in aqueous solution.
· Example: Acetic Acid (CH3COOH), Nitric Acid (HNO3), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), etc.
· Strong Acid is an acid that is completely ionized in water and produces (H+) . Examples: Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3),Hydrochloric acid (HCl),
· Weak Acid is an acid which is partially ionised in water and thus produces a small amount of hydrogen ions (H+) is called a . Example: Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
BASES:-
· Bases are bitter
in taste and soapy to touch
·
All the bases are not soluble in water.
·
Those bases which are soluble in water are known as alkalis.
·
They
turn blue litmus to red.
·
Conducts electricity in solution.
·
Release OH– Ions in Aqueous Solution
INDICATORS:-
· An indicator is a substance that changes colour when added to an Acid or
base. If there is no change then it is said to salt or neutral.
· There are two types of indicators Natural Indicators and Synthetic
Indicators.
Natural Indicators
Litmus:-
· Litmus is a natural dye that is extracted from lichens, a plant belonging
to the division Thallophyta.
·
Litmus solution is prepared from this extract.
·
It has a mauve (purple) colour in distilled water.
·
It is available in the form of a solution, or in
the form of strips of paper, known as litmus paper.
IT ·These are available as red and blue litmus paper.
China rose:-
· China rose is a flower also called as hibiscus.
· It is prepared by soaking the petals of the flower in water.
· In an acidic substance, it changes itself to dark pink or magenta colour.
· In basic substance it changes itself to green.
Turmeric:-
· Turmeric is another natural indicator.
· It is made with turmeric paste.
· It is also available in paper strips.
· It remains yellow in acidic substances.
· It turns brownish-red colour on the basic solution.
RRed Cabbage:
· Juice of red cabbage is purple
in color. it turns reddish with acid and turns greenish with
base.
Synthetic Indicators
Phenolphthalein:-
· Phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solution.
· Turns pink in base solution.
Neutralisation
· The reaction between acid and base is called neutralization.
· Salt and water are produced in this process with the evolution of heat.
· Acid + Base → Salt + Water (Heat is evolved)
Example:-
Hydrochloric
acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water
HCl
+ NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Olfactory indicator
Olfactory indicators are substance whose smell varies depending on whether it is mixed with an acidic or basic solution .
example; vanilla, Onion, etc.
Reaction
of metal with acid:
·
Metal react with dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
displaces hydrogen atoms from the acids as hydrogen gas and forms a compound
called a salt. Example:
Acid
+ Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
· we hear a pop sound. When a matchstick is brought near the mouth of the tube containing the product of the reaction. It is the hydrogen gas that burns with a pop sound.
·
Magnesium reacts with dilute
hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and hydrogen.
·
Zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas is evolved.
·
Sodium reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form sodium sulphate and hydrogen gas is evolved.
Reaction of Metal
Carbonates and Metal Hydrogen carbonates react with Acids
· Metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids to give a corresponding salt, water and carbon dioxide.
· Both the reaction produces CO2 which further on passing through lime water makes lime water milky due to formation of calcium carbonate.
· On passing excess carbon dioxide below reaction occurs.
Reaction of acids
and bases React with each other:
·
Reaction between an acid and a base to gives a salt and water . It is known as a neutralization reaction. generally, a
neutralization reaction can be represented as –
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
· H(+) cation of the acid combines with the
OH(-) anion of the base & form water. A compound formed by the cation of the
base and the anion of the acid is called a salt.
HCl(aq) + KOH (aq) → H2O(ℓ) + KCl (aq)
2 HCl (aq) + Mg(OH) 2(aq)
→ 2 H2O(ℓ) + MgCl 2(aq)
3 HCl (aq) +
Fe(OH) 3(s) → 3 H2O(ℓ) + FeCl 3 (aq)
HCl(aq) +
NaOH(aq) → H 2O(ℓ) + NaCl(aq)
Reaction of Acid with Metal Oxides:
·
Metal oxides are basic in nature. when an
acid reacts with a metal oxide both neutralize each other & respective salt and water are formed as product.
Acid + Metal Oxide →
Salt + Water
·
Metal oxides are basic in nature.
1.
2HCl+CuO⟶CuCl2+H2O
2.
H2SO4(aq) + CuO(s) → CuSO4(aq)
+ H2O(l)
3.
2HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(s) → MgCl2(aq) +
2H2O(l)
4.
2HNO3(aq) + CuCO3(s) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
WHAT DO ALL
ACIDS AND ALL BASES HAVE IN COMMON?
·
All acids gives hydrogen gas on reacting with
metals, so hydrogen seems to be common to all acids.
·
The electric current is carried out in acidic solution by ions.
·
Acids contain H+ ion as cation and anion such as
Cl– in HCl, NO3 – in HNO3 , SO2– 4 in H2 SO4 , CH3COO– in CH3COOH. Since the
cation present in acids is H+ , this suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions,
H+ (aq), in solution.
What Happens
to an Acid or a Base in a Water Solution?
·
H+ in HCl is produced in the
presence of water. The separation of H+ ions from HCl molecules cannot take place in
the absence of water.
· HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
Hydrogen ions cannot exist alone, but they exist after combining with water
molecules.
·
Thus hydrogen ions must always be shown as H+
(aq) or hydronium ion (H3O+ ). H+
·
+ H2O → H3O+ We have seen that acids
give H3O+ or H+ (aq) ion in water.
Base:
- Most of them are insoluble in water.
Alkali:
- Aqueous solution of an alkali is a solution of a base, (mainly
metallic hydroxides).
- It dissolves in water and dissociates to give OH− ion.
- All alkalis are bases but revers is not true ,all bases are alkalis.
HOW STRONG
ARE ACID OR BASE SOLUTIONS?
·
A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration
in a solution, called pH scale. The p in pH re-presents ‘potenz’ in German, Which means power.
·
On the pH scale, we can measure pH generally from
0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
·
pH number of solution, only indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution.
·
Higher the hydronium ion concentration, the lower is
the pH value.
·
The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
· As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents an increase in OH– ion concentration in the solution, that is, an increase in the strength of alkali.
Importance
of pH in Everyday Life
pH sensitivity of plants and animals
Plants and animals are sensitive to pH. Many life processes such as the functions of enzymes and hormones, digestion of food, happen at a certain pH value. The digestion process happens at a specific pH in our stomach which is 1.5 to 4.
pH of a soil
The pH of soil should be optimum for the growth of plants /crops is 6.5 to 7.0.
pH in tooth decay
Tooth decay arises when the teeth are exposed to an acidic
environment of pH value lower than 5.5 .
pH of
self-defence by animals and plants
Acidic environments are used by animals and plants as a self-defence
mechanism. For example, bee and plants like nettle secrete a highly acidic
substance for self-defence. These secreted acidic substances have a specific
pH.
pH value of
Salts
·
Salts produced by strong acid and a strong base are
neutral with pH value of 7.
·
Salts produced by strong acid and weak base are acidic
with pH value less than 7 .
·
Salt produced by strong base and weak acid are basic in
nature, with pH value more than 7.
Manufacture
of acids
Non-metal oxide + water → acid
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
SO3(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(aq)
4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 4HNO3(aq)
Non-metal oxides are acid anhydrides.
Hydrogen + halogen → acid
H2(g) + Cl2(g) →
2HCl(g)
HCl(g) + H2O(l) →
HCl(aq)
Metallic salt + conc. sulphuric acid → salt + more
volatile acid
2NaCl(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
2KNO3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2HNO3(aq)
Manufacture
of bases
Metal + oxygen → metallic oxide (base)
4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
2Mg(s) + O2(g) →
2MgO(s)
Metal + water → base or alkali + hydrogen
Zn(s) + H2O(steam)
→ ZnO(s)+ H2(g)
Few metallic oxides + water → alkali
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) →
2NaOH(aq)
Ammonia + water → ammonium hydroxide
NH3(g) + H2O(l) → NH4OH(aq)
Preparation
of Sodium hydroxide
Chemical formula – NaOH (caustic soda)
Bleaching
powder
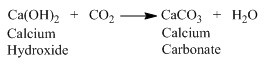
Chemical formula – Ca(OCl)Cl or CaOCl2
Preparation – Ca(OH)2(aq)+Cl2(g)→CaOCl2(aq)+H2O(l)
Baking
soda
Chemical name – Sodium hydrogen carbonate -NaHCO3
Preparation
method
Limestone is heated:
CaCO3→CaO+CO2
CO2 is
passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride and ammonia:
NaCl(aq)+NH3(g)+CO2(g)+H2O(l)→NaHCO3(aq)+NH4Cl(aq)
Uses:
1. Textile industry
2. Paper industry
3. Disinfectant
Washing soda
Chemical name – Sodium hydrogen carbonate
chemical formula: NaHCO3
Preparation
Limestone is heated: CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Carbon dioxide is
passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride and ammonia to obtain washing soda:
NaCl(aq) + NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) →
NaHCO3(aq) + NH4Cl(aq)
Uses
1. In glass, soap and paper industries
2. Softening of water
3. Domestic cleaner










Social Plugin