We are presenting CBSE NOTES FOR QUICK REVISION
, It will help you to focus your attention and avoid distractions. As you read notes, you will be engaging your mind in identifying and organizing the main ideas of topic in minimum time span and make it easy to memorize the topic for best result.We have also added CBSE MCQ Questions with answer in MCQ quiz format for your self assessment.
PHYSICAL CHANGE:-
·
A kind of changes in which a substance
undergoes a change in its physical properties is called a physical change.
·
Properties such as colour, shape, size and state of substance are
called physical properties.
·
A physical change is generally
reversible
·
In physical change where no new
substance are formed.
·
The chemical properties of the
substance doesn’t change.
CHEMICAL CHANGE:-
·
A kind of change in which a substance
undergoes a change in its chemical properties is called a chemical change.
Means totally a new substance is formed.
·
The chemical change is
irreversible .It is permanent.
·
During chemical change heat,
light, sound or gas may produce.
·
A change in colour or smell may
occur.
·
Following are example of
chemical change-
Ø Burning
of paper
Ø Burning
of wood
Ø Burning
of coal
Ø Burning
of magnesium ribbon
Ø Making
of curd from milk
Ø Digestion
of food
Ø Ripening
of fruits
Ø Bursting
of a cracker
Ø Boiling
of egg
Chemical reaction
·
Chemical change is
also known as chemical reaction.
Burning of magnesium ribbon:-
· Burning of magnesium :Magnesium reacts with oxygen and
form magnesium oxide in air.
·
The word-equation for the above reaction would
be –
Magnesium +
Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
·
The substances that undergo chemical change in
the reaction (1.1), magnesium and oxygen, are the reactants.
·
The new substance, magnesium oxide, formed
during the reaction, is the product.
· In word-equation change of reactants to products is shows through an arrow placed between them.
· Reactants are written on the (LHS) with a plus sign (+) between them.
· Products are written on the (RHS) with a plus sign (+) between them.
·
The arrowhead pointing towards the products, Which shows the direction of the reaction
Writing a Chemical Equation
·
Chemical equation can be written by using chemical
symbols of reactants and products instead of their names.
Mg + O2 → MgO
·
Is the number of atoms of each element the same
on both the sides equal? If not, then the equation is unbalanced because the
mass is not the same on both sides of the equation. Such a chemical equation is
a skeletal chemical equation or unbalanced chemical equation for
a reaction.
· A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element of reactants is equal to that of products, is called a balanced chemical equation.

Balancing a Chemical Equation
·
Equalizing the number of atoms of each element on
reactants and products sides of a chemical equation is called balancing a
chemical equation.
·
The word-equation for may be represented as –
Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
·
The above word-equation may be represented by
the following chemical equation –
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
·
Counting the number of atoms in reactants and
product side
|
Element |
Number of atoms reactants
(LHS) |
Number of atoms in
products (RHS) |
|
Zn |
1 |
1 |
|
H |
2 |
2 |
|
S |
1 |
1 |
|
O |
4 |
4 |
·
As the number of atoms of each element is the
same on both sides of the arrow, chemical is a balanced chemical equation.

TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Ø Combination
Reaction
Ø Decomposition
Reaction
Ø Displacement
Reaction
Ø Double
Displacement Reaction
Ø Oxidation
and Reduction Reaction
Combination Reaction
Ø A reaction in
which two or more substances combine together to form a single product is known
as a combination reaction.
Ø
The combination reaction is often called synthesis.
Ø
Example:
1. Calcium
oxide reacts with water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide)
releasing a large amount of heat.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
In the above reaction, calcium oxide and water react to form
a single product, calcium hydroxide. This kind of reaction in which a single product
is formed from two or more reactants is known as a combination reaction.
2. Formation
of water from
H2(g) and O2(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g)
→ 2H2O(l)
3. Burning
of coal
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
Decomposition Reaction
Ø Reactions in
which a single substance breaks down to form two or more substances, is called
a decomposition reaction.
Ø Decomposition
of calcium carbonate (Limestone) to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide on
heating is an important decomposition reaction used in various industries.
Calcium oxide is known as lime or quick lime. It has many uses one is in the manufacture of cement. If decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, it is called thermal
decomposition.
CaCO3(s) ⎯
→ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Ø Decomposition of
FeSO4 on heating.
2FeSO4(s) ⎯
→ Fe2O3(s)
+ SO2(g) + SO3(g)
Displacement Reaction
Ø
The reaction in which one atom or a group of atoms
of a compound is replaced by another atom, is called a displacement reaction.
Ø Generally, a
more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution in
displacement reaction.
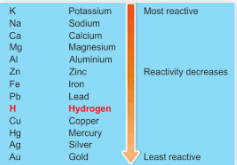
Ø The series in
which metals are arranged in the decreasing order of their reactivity is called
activity series of metals.
Activity series of metals.
FOR EASTING REMEMBERING THE REACTIVITY
SERIES:

Examples of displacement reaction
Ø
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq)
+ Cu(s)
In above reaction, iron has displaced or removed another
element, copper, from copper sulphate solution. This reaction is known as
displacement reaction
Ø
Other examples of displacement reactions are
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq)→ ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq) + Cu(s)
Zinc and lead both are more reactive elements than copper and They
displace copper from its compounds
Double Displacement Reaction
Ø
The reaction in which anions and cations of two different
molecules exchange places, forming two completely different compounds, is
called double displacement reaction. For example,
Na2SO4 (aq)
+ BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Oxidation
and Reduction
Oxidation: If any substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen
in a reaction, the substance is said to be oxidized and the reaction is known as
oxidation.
Oxidizing Agent: If any substance oxidizes the other substance gets reduced, then
It is
known as an oxidizing agent.
Ø
The surface of copper powder becomes coated with
black copper(II) oxide.
Ø
Why has this black substance formed?
Ø
This is because oxygen is added to copper and
copper oxide is formed.
2Cu + O2 →
2CuO
Ø
This is called oxidation reaction.
Ø If a
substance gains oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be oxidised.
Ø If a
substance loses oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be reduced.
Reduction: If any substance loses oxygen and gains hydrogen in a reaction,
the substance is said to be reduced and the process involved is known as
reduction.
it is
known as a reducing agent.
Ø
Example of reduction reaction
2 Na + H2S → Na2S + H2
Redox reaction:
Ø In redox rection,Oxidation
and reduction reaction taking place simultaneously
CuO+H2 →Cu+H2O
During above reaction the copper(II) oxide is losing
oxygen and is being reduced. The hydrogen is gaining oxygen and is being
oxidised.
HAVE YOU OBSERVED THE EFFECTS OF OXIDATION REACTIONS IN EVERYDAY
LIFE? Y LIFE?
Ø
Oxidation has a damaging effect on metals as
well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metals is studied as
corrosion, and that on food is studied as rancidity. Thus, two common effects
of oxidation reactions observed in daily life are corrosion of metals and rancidity of food
Chapter test


Social Plugin