Soil
·
Soil
is considered as one of the most important natural resources.
· Soil is mixture of rock particles and humus .
·
It gives anchorage to the plants and supplies water and nutrients.
·
Soil is the native (home) for many organisms.
·
Soil
is essential for agriculture which provides food, clothing and shelter
for all.
Soil Profile
·
Soil
is composed of many different layers.
· Rotting dead matter in the soil is known as humus.
· Soil is formed by the process of weathering which involves breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate.
·
The
nature of soil depends upon the rocks from which it has formed and the
type of vegetation that grows in it.
· Soil profile is a vertical section through different layers of the soil .
· Each layer differs in chemical composition ,feel (texture), colour and depth .
·
These
layers are known as horizons. Soil is fertile and provides nutrients to
growing plants.
·
A
A-horizon: A-horizon layer is generally soft, porous and can retain more water. It is known as topsoil or the A-horizon.
· The next layer is called the B-horizon or the middle layer,Which has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals. This layer is generally harder and more compact .
· The C-horizon is the third layer of soil , that is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices.
· Bedrock which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade. It is bottom layer of soil.
Soil types
·
Weathering
of rocks results production of small particles of various materials. which include include sand and
clay.
·
The
proportion of sand and clay depends upon the rock from which the particles
were formed, that is the parent rock.
·
Living
organisms( bacteria, plant roots and earthworm ) are also important parts
of any soil.
·
The
soil is classified on the basis of the ratio of particles of various
sizes.
·
If
soil containing greater proportion of big particles it is called sandy soil.
·
If
the ratio of fine particles is relatively higher, then it is called clayey
soil.
·
If
the amount of large and fine particles is same, then the soil is
called loamy.
·
Thus,
the soil can be divided in categories as sandy, clayey and loamy.
Sandy
Soil
·
The
size of the particles in a soil has an affects on its properties.
·
Sand
particles are quite large.
·
They
cannot fit close together, so there are large spaces/gaps between them.
·
These spaces/gaps are filled with air.
· Sand is well aerated due to spaces between the particles.
· Due to this water can drain quickly through the spaces between the sand particles.
·
sandy soils tend to be light, well aerated and rather dry.
Clayey
Soil
·
Clay
particles are much smaller, pack tightly together, leaving little space for
air.
· It can be held water in the tiny gaps between the particles of clay.
·
Clayey soils have less air.
· It are heavy as they hold more water than the sandy soils.
Loamy
Soil
· It is the best topsoil for growing plants is loam.
· It is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as
silt.
·
The
loamy soil also contains humus in it.
·
It
has the enough water holding capacity for the growth of plants.
Silt
·
Silt
occurs as a deposit in riverbeds.
·
The
size of the silt particles is between sand and clay.
Properties of Soil
Percolation
rate of water in soil
· The property of absorption of water by soil is called percolation . Amount of water absorbed by soil is called as percolation.
·
The
amount of water absorbed by soil in a given interval of time is known ass
percolation rate. And it’s formula is :-

For
example, suppose that for a certain sample, it took 20 minutes for 200 mL to
percolate.
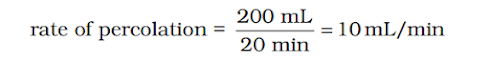
Moisture in Soil
· Moisture is measured by the quantity of water present in the soil. Even though dry soil contains a small amount of moisture. Clayey
soil retains the highest amount of moisture.
Absorption of water by Soil
·
·
How
much Soil absorbed can be found by :-
Initial
volume of water in the measuring cylinder = U mL
Final
volume of water in the measuring cylinder = V mL
Volume
of water absorbed by the soil = (U – V) mL
Weight
of water absorbed by the soil = (U – V) g
(1 mL of water has weight equal to 1 g)
Soil
and Crops
·
Different
types of soils are found in different region of India.
·
In
some regionss there is clayey soil, in some parts there is loamy soil while in
some other parts there is sandy soil.
·
Soil
is influenced by wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity.
·
The
climatic factors and the components of soil, determine the different types of vegetation and crops that might grow in any region.
·
Clayey
as well as loamy soils are both suitable for growing cereals like wheat, and gram.
This kind of soils are good at retaining water.
·
For
paddy crop, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good retaining capacity of water are ideal.
· loamy soils, which drain water easily, are good for lentils (masoor) and other pulses.
· Sandy or loam, which drain water easily and can hold plenty of air, are more suitable for cotton.
·
Crops
such as wheat are grown in the fine clayey soils, because they are rich in
humus and are very fertile.




Social Plugin