Introduction
- The earth’s crust contains only 0.02% carbon in minerals form (like carbonates,hydrogen carbonates, coal and petroleum) and the atmosphere contains 0.03% of carbon dioxide.
- Carbon is a very common “ingredient” of matter it can combine with itself and with many other elements.
- Carbon is the only element that can form so many different compounds an have billion of compound.
Bonding in carbon - The covalent bond
- Carbon atom has four valence electrons, so it can achieve octate by forming four covalent bonds.
- A carbon atom form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms or with other elements atoms .
- When Carbon atom bonds only with hydrogen, it forms compounds which is called hydrocarbons.
- Carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity and have low boiling and melting points of the carbon compound.
Allotropy of carbon
The phenomenon of existence of an element in two or more forms which have identical chemical properties but different physical is known allotropy.
- The forms of element is known as allotropes.
- Carbon has two well known allotropes which are graphite and daimond.
- In diamond, each carbon atoms forming a rigid three dimensional structure by bonding with three other carbon atoms.
- In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded through covelent bond to three other carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array.
- Graphite structure is formed by the hexagonal arrays being placed in layers one above the other.
- These two different structures result in diamond and graphite having very different physical properties even though their chemical properties.
- Diamond is the hardest material known while graphite is smooth and slippery material. Graphite is also a very good conductor of electricity however it is non-metals.
Versatile nature of carbon
- Carbon is a piculier element and is found in many different chemical compounds.
- Carbon atom has ability to form single, double, and triple bonds. It can also form chains, branched chains, and rings when connected to other carbon atoms. It is very verstile substance.
- The two characteristic features of carbon atom, tetravalency and catenation made it versatile .
- This put together gives rise to a large number of compounds. Many have the same non-carbon atom or group of atoms attached to different carbon chains.
Why Carbon Is Special ?
There are about ten million organic compounds known by chemists.
Carbon is the only element that can form so many different compounds because
- Carbon atom can form four chemical bonds to other atoms.
- Carbon atom is small size to fit in comfortably as parts of very large molecules
1.Catenation
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings.
In addition, carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
Carbon Compounds which are formed by only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called saturated compounds.
Carbon Compounds having double or triple bonds between their carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds.
ii.Small atomic size of Carbon atom
Carbon has a valency of four, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element.
Compounds of carbon are formed with oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine and many other elements giving rise to compounds with specific properties which depend on the elements other than carbon present in the molecule.
The bonds that carbon forms with most other elements are very strong making these compounds exceptionally stable due to this reason for the formation of strong bonds by carbon is its small size. This enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of electrons strongly
Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
Saturated Carbon Compounds
A saturated organic compound contains single bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkanes is an important class of saturated compounds are the .
The suffix of all alkanes end with -ane.
ALKANES :They are also known as parrafins.
- CH4 = methane = one hydrogen-saturated carbon
-
- C2H6 = ethane = two hydrogen-saturated carbons
-
- C3H8 = propane = three hydrogen-saturated carbons
- C4H10 = butane = four hydrogen-saturated carbons
- C5H12 = pentane = five hydrogen-saturated carbons
- C6H14 = hexane = six hydrogen-saturated carbons
Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
Hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms are known as unsaturated Carbon Compounds.
- Alkenes
- Alkynes
The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contain one or more double bonds are known as alkenes.
General formula : CnH2n
The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contains one or more triple bonds are known as alkynes.
General formula : CnH2n-2
Isomer
Carbon atoms can forms verites of compounds with different type arrangement, by long chain arrangement, branched chain arrangement and cyclic chain arrangement of carbon atoms.
Hydrocarbons have same molecular formula but differen structural arrangement of atoms are called Structural Isomers.
The smallest hydrocarbon that has isomers is butane, which has only four carbon atoms. Structural formulas for normal butane (or n-butane) and its only isomer, named iso-butane. Both molecules have four carbon atoms and ten hydrogen atoms (C4H10), but their atoms are arranged differently in the two compounds.
Four carbon atoms are arranged in a straight chain In (n-butane),. In iso-butane, one of the carbon atoms branches off from the main chain arrangement.
Normal butane(N-butane)
Iso-butane
IApart from straight and branched carbon chains, some compounds have carbon atoms arranged in the form of a ring. example, cyclohexane,which has the formula C6H12 and have following structure
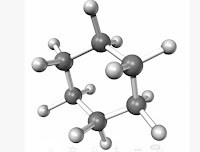
Homologous series
Carbon behaves like a very friendly element.
Carbon also forms bonds with other elements such as halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur.
if in a hydrocarbon chain, one or more hydrogens is replaced by these elements(halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur.), such that the valency of carbon remains satisfied. Than the element replacing hydrogen is referred to as a heteroatom.
A homologous series refers to a group of compounds that share similar properties.
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds (compounds that contain C atoms) that differ from each other by one methylene (CH2 ) group.
Each member of a homologous series is called a homologue .Example, methane and ethane are homologues and belong to the same homologous series. They differ from each other by one CH2 group. The formula of methane is CH4 and the formula of ethane is C2 H6.
Functional group & CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON COMPOUNDS
In saturated hydrocarbon , carbon atoms are joined by only a single bond. Saturated hydrocarbons are unreactive, but when another ‘atom’ or ‘group of atoms’ is included in compound , the resulting molecule becomes highly reactive. The other ‘atom’ / ‘group of atoms’ in a carbon compound is called a functional group.
A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that makes a carbon compound or an organic compound reactive and determines its properties.
Some functional groups in carbon compounds
| Hetro atom | Class of compound | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Cl/Br | Halo (cholro/Bromo) | -Cl / -Br |
| O (OXYGEN) | Alcohol | -OH |
| O (OXYGEN) | Aldehyde | -COH |
| O (OXYGEN) | Kitone | -C=O |
| O (OXYGEN) | Carbocylic acid | -COOH |
Combustion:Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light.
- (i) C + O2 → CO2 + heat and light
- (ii) CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light
- (iii) CH3CH2OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light
Saturated hydrocarbons gives a clean flame while unsaturated carbon compounds gives a yellow flame with lots of black smoke.
Oxidation: Oxidation of ethanol in presence of oxidizing agents gives ethanoic acid.










Social Plugin