CBSE CLASS 7-Reproduction in Plants -CHAPTER NOTE
All
living organism including plants, is to create offspring for the next
generation.
Most
plants have roots, stems and leaves. These parts are called the vegetative parts of a
plant.
After
a certain period of growth, most plants bear flowers and gives fruits.
When we eat fruit we discard the seeds in it. Seeds germinate and form new
plants.
All living organisms have a characteristic to produce same kind of living organisms.
Production of new individuals from a parent is known as reproduction.
Flowers
perform the function of reproduction in plants. Flowers are the reproductive
parts.
MODES OF REPRODUCTION
There
are several ways by which plants produce their offspring. These are categorized
into two types:
1.
Asexual
reproduction
2.
Sexual
reproduction
Asexual reproduction
·
In asexual reproduction we only need one parent to produce a offspring.
Vegetative propagation: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which plant reproduce by the help of different vegetative parts like roots, stem, leave etc.
Budding:
·
Yeast
grow and multiply every few hours if sufficient nutrients are made available to
them.
·
Yeast
is a single-celled organism.
·
A small bulb-like projection emerging out from the yeast cell is called a bud.
·
A bud gradually grows in mature state and gets detached from the parent cell.
·
A new yeast cell grows, matures and produces more yeast cells.
·
A few times, another bud arises from the bud forming a chain of buds.
· This process continues and a large number of yeast cells are produced in a short
time.
Fragmentation
·
Green
patches in ponds, or in other stagnant water bodies. These are the algae.
· When a algae gets water and nutrients algae grow and multiply rapidly by fragmentation.
·
An
alga breaks into two or many fragments. These pieces grow into
new individuals.
·
This
process continues and cover a large area in a short period of time.
Spore formation
·
A fungi on bread piece grow from spores which are present in the air.
·
When
spores burst out they keep floating in the air.
·
As
they are light they can cover long distances.
· Spores are asexual reproductive bodies. Each spore is covered by a hard protective coating to withstand unfavorable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. that is why , they could survive for a long time. Under a favorable and good condition, a spore germinates and develops into a new individual. Example:- moss and ferns
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
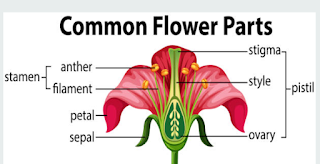
·
Flowers
are reproductive parts of a plant. Stamens are male reproductive part
and pistil is female reproductive part.
·
Flowers which have either stamen or pistil are called unisexual flower. Ex-
Corn, papaya and cucumber produce unisexual flowers,
·
Flowers
which has both stamen and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Ex- mustard,
rose and petunia.
·
Both
Reproductive parts male and female unisexual flowers may be present in the same
plant or in different plants.
·
Anther
has 'pollen grains' which produce male gametes.
· A pistil has three parts style, stigma and ovary.
·
Ovary
contains one or more ovules.
· Female gametes are formed in an ovule.
·
In the sexual reproduction a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote.
Pollination
· Pollination is a process of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma.
Plants can be:
- Self-pollinating - the plant which can fertilize itself
- Cross-pollinating - the plant which needs a
vector (a pollinator or the wind) to get the pollen to another flower of
the same species.
Fertilization
· The process in which male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote is called fertilization.
·
The
zygote develops into an embryo.
FRUITS
AND SEED FORMATION
·
After the process of fertilization, the ovary grows into a fruit and other parts of the flower fall
off.
·
The
fruit is the ripened ovary.
·
The
seeds develop from the ovules. The seed contains an embryo which is enclosed in a protective
seed coat.
SEED
DISPERSAL
· The process in which seed disperse to different places is called seed dispersal.
· Seed dispersal is done by wind, water and animal. It help the plants to (i) prevent overcrowding, (ii) avoid competition for sunlight, water and minerals and (iii) invade new habitats.


Social Plugin